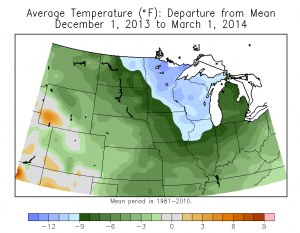
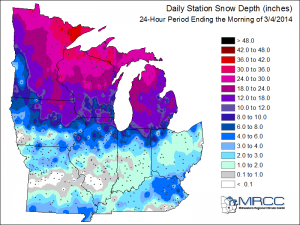
Climate and weather greatly impact a farmer’s day-to-day operations as well as their livelihood. To gain perspective on farmers’ production practices and how they are changing, Michigan State University Extension educators and specialist invited farmers from across Michigan to participate in one of three discussions on sustainable corn production held at locations in the north central, central and south central part of the state during mid-March. Climate and nitrogen were two of the topics discussed.
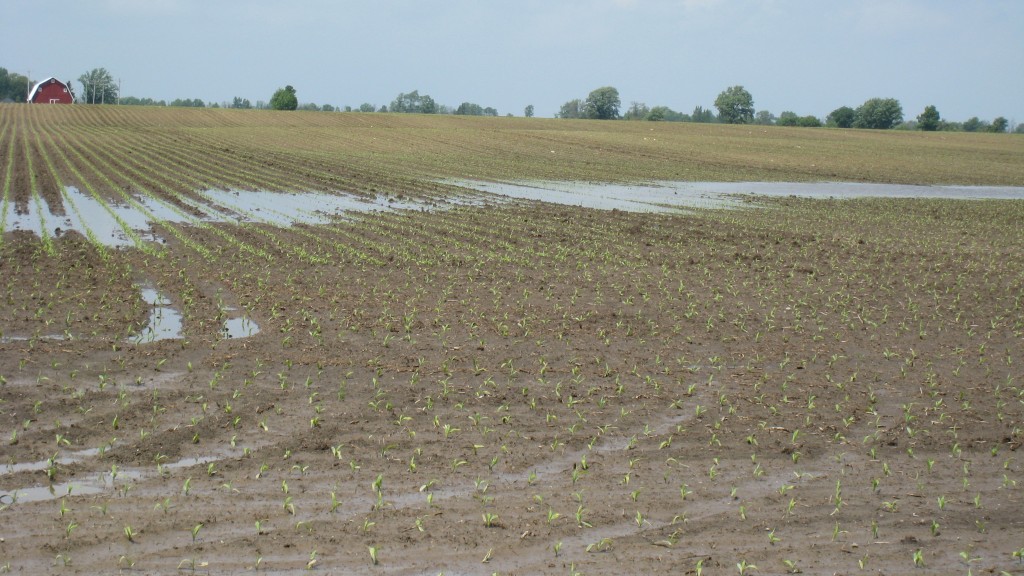

Concerns over heavy spring rains prompts Michigan corn growers to split N-applications throughout growing season.
We found that producers have already decreased the amount of nitrogen applied per bushel of yield. Cost of nitrogen, concern of environmental impacts, improved technology and better information were all given as reasons for the change. The source of nitrogen used is also changing. Most producers indicated that they will or have already moved away from using anhydrous mostly due to availability. Continue reading